About this Page
The On-demand backup page, accessed via the Revyz Configuration Manager path, allows administrators to initiate a targeted and immediate backup of their critical Jira configurations.
What is the use case?
The On-demand backup feature is primarily used for creating an immediate, user-defined restore point for your Jira configurations in response to planned changes or critical administrative events. Creating an immediate restore point for your Jira configurations before implementing major administrative changes, or right after completing a critical configuration rollout to capture a known good state.
Jira Configurations: On Demand Backup
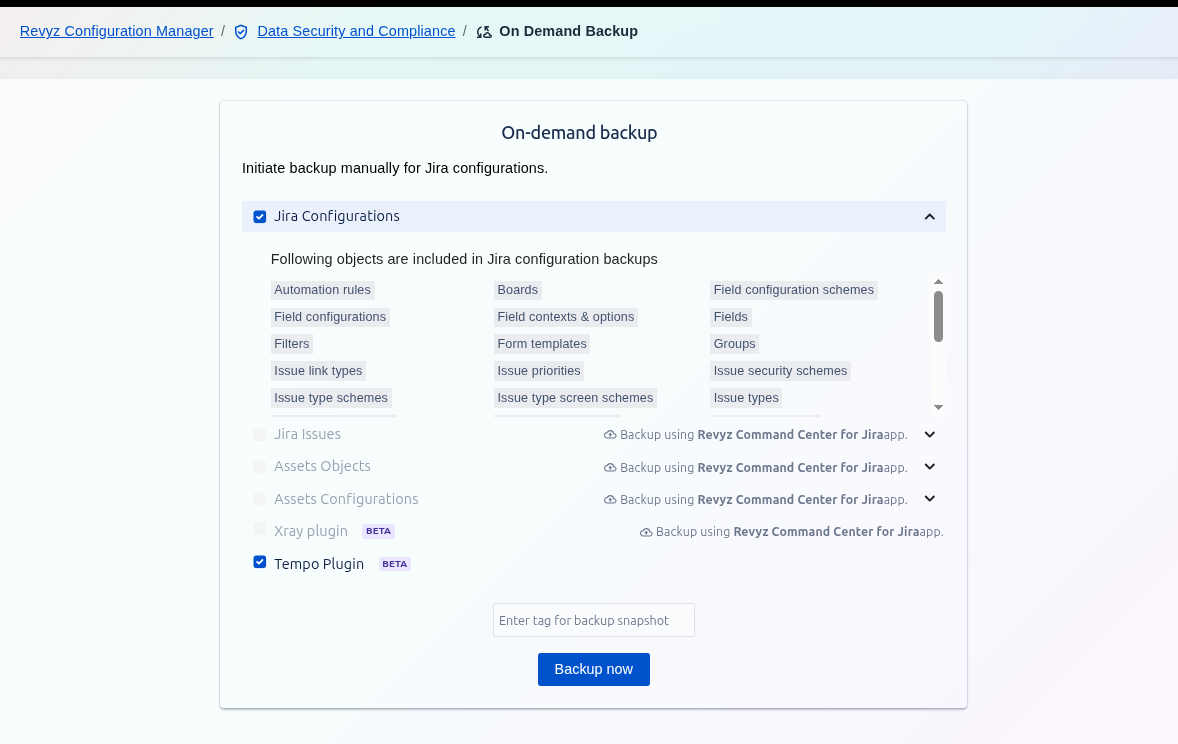
Selecting the Jira Configurations option creates a backup of the essential administrative and project-level settings that govern the structure and behavior of your Jira instance. This backup does not include the individual Jira issues themselves but focuses on the framework that supports them.
Restoring these configurations is critical for rebuilding your environment or migrating to a new instance.
Included Objects in Jira Configuration Backups
The following configuration objects are included in this backup:
-
Automation rules: All global and project-level automation rules you have configured.
-
Boards: Agile boards (both Scrum and Kanban), including their column configurations, quick filters, and swimlanes.
-
Field configuration schemes: Schemes that associate field configurations with issue types for specific projects.
-
Field configurations: Settings that define the behavior of fields, such as whether they are required, hidden, or have a specific renderer.
-
Field contexts & options: Custom field contexts and the specific options available for select list-type fields.
-
Fields: All custom fields created in your instance.
-
Filters: Saved JQL filters used for boards, dashboards, and subscriptions.
-
Form templates: Templates used for issue creation and other forms.
-
Groups: User groups that are used in permission schemes, security levels, and sharing filters.
-
Issue link types: The different ways issues can be linked to each other (e.g., "blocks," "relates to").
-
Issue priorities: The priority levels available for issues (e.g., Highest, High, Medium).
-
Issue security schemes: Schemes that control which users or groups can view specific issues.
-
Issue type schemes: Schemes that define which issue types are available for a project.
-
Issue type screen schemes: Schemes that map issue operations (like create, edit, view) to specific screens for different issue types.
-
Issue types: All standard and custom issue types (e.g., Story, Bug, Task, Epic).