About this Page
The Notifications Audit Log tracks all administrative changes made to the configuration of system notifications, inclusions, and exclusions for backup and restore jobs.
What is the use case?
The primary use case is change management and governance. This log is critical for:
-
Auditing Configuration Changes: It tracks who made specific changes to what data is included in backups (e.g., adding a project) or excluded from them, and when these changes happened.
-
Monitoring Alert Settings: It records any edits to the Notification Settings, which define when administrators receive critical alerts about job status (started, completed, failed, etc.). This ensures compliance with alerting protocols.
-
Troubleshooting: If a backup job fails or includes/excludes the wrong data, this log helps quickly identify the last configuration change that may have caused the issue.
This feature is applicable to:
Command center for jira config manager for jira assets data manager for jira
How to view Audit Logs for Notifications?
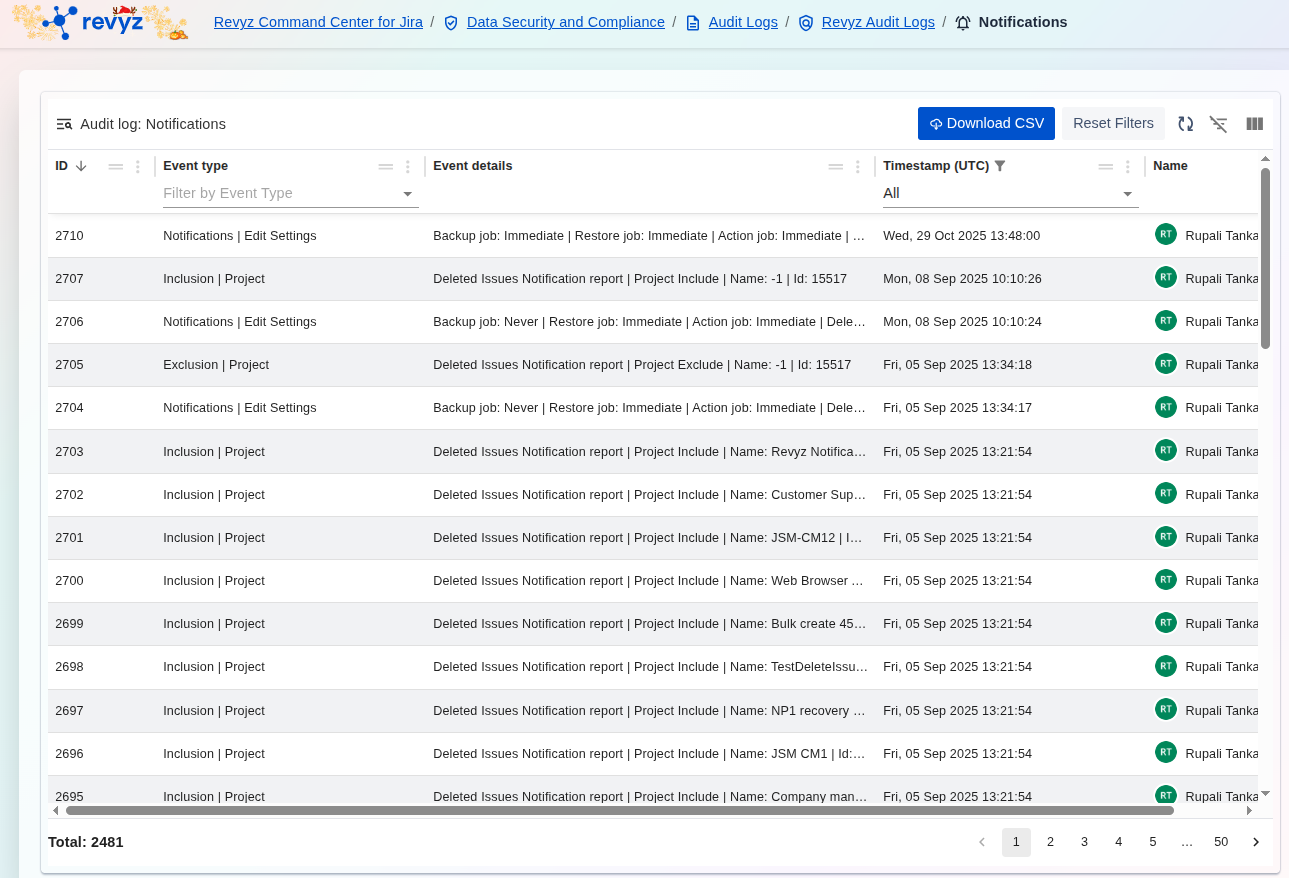
ey Event Types Tracked
The Event Type column reveals the three main activities recorded:
-
Notifications | Edit Settings: Records changes to the application's global notification parameters, such as defining job statuses that trigger alerts (e.g.,Backup job: Immediate | Restore job: Immediate). -
Inclusion | Project: Logs the action of adding a specific project to the list of data to be included in backup or restore operations. The details show the specific project name and ID that was added. -
Exclusion | Project: Logs the action of removing a project from the inclusion list, effectively excluding it from backup or restore operations.
Accountability and Details
-
Event details: Provides granular context for the change. For
Inclusion | Projectevents, it lists the exact project name and ID being included (e.g.,Project Include | Name: Revyz Notifications). ForNotifications | Edit Settings, it details the new notification frequency or status settings. -
Name: The Name column consistently identifies the user responsible for making the configuration change.
-
Timestamp (UTC): Provides the exact time the configuration was modified, which is essential for change management rollback and troubleshooting.
The log clearly shows a detailed history of both alert settings and project scoping changes, giving administrators full control over their data management policies.